|
MONTESSORI CORAL REEF FIELD GUIDE INDEX
and
INTRODUCTION
INVERTEBRATES
Cnidaria
(PHYLUM)
Jellyfishes - Sea Jellies
|
|
Scyphozoans (Class) |
|
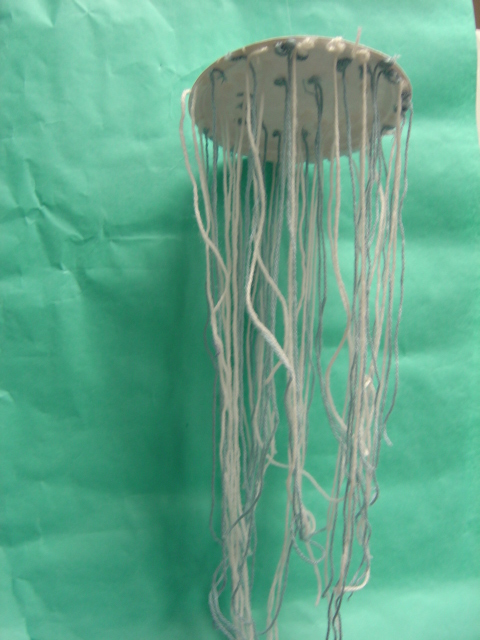 |
| Habitat: Atlantic coast Size: up to 40
cm across
Food: zooplankton, including other jelllyfish
Interesting Fact: They are soft gelatinous (like jelly) and mostly
transparent (you can see through them).
|
|
| Purple Jellyfish |
Other Sites:
Coelentrates
New Jersey Scuba Diver - Jellies |
|
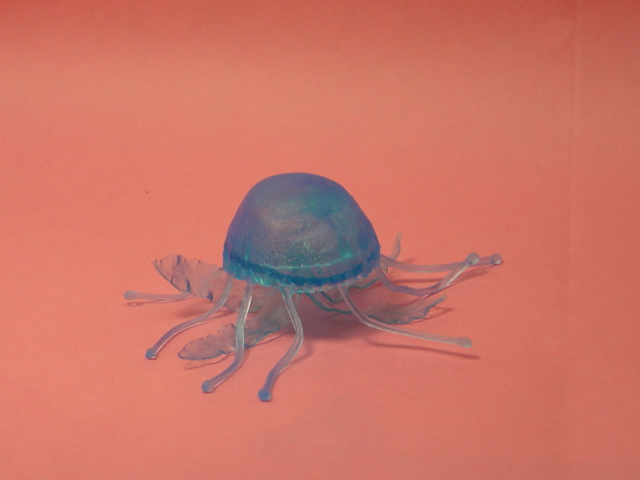 |
| Habitat: Off the coast of California Size:
Bell up to 3 feet in diameter.
Food: fish and zooplankton.
Interesting Fact: It is purple; my favorite color. It has a nasty sting.
Nia: Monterey Bay Site |
|
| Purple-striped Jellyfish |
Other Sites: |
|
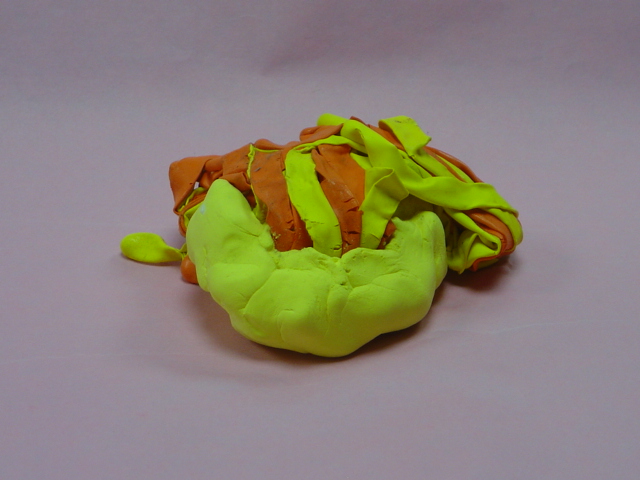 |
| Habitat: shallow water; often in mangrove swamps;
Caribbean, Indo-Pacific Size: to 12 inches wide; 2
inches high
Food: carnivorous; algae and plankton
Interesting Fact: Its flattened bell rests on the sea bottom and its tentacles float upward.
|
|
| Upside down Jellyfish |
Other Sites:
Upside down Jellyfish |
|
 |
| Habitat: Caribbean Size: Medusa - 3 feet in
diameter. Tentacles to 70 feet
Food: moon jellies
Interesting Fact: These giants have drifted into the Gulf of Mexico and eating moonjellies there.
|
|
| Caribbean Pink Jellyfish |
Other Sites: |
|
 |
| Habitat: Chesapeake Bay Size: 9-10"
bell with 5 to 6 feet long tentacles
Food: comb jellies
Interesting Fact:
Scientists think that East Coast Sea Nettles protect oysters from comb jellies, one of their predators.
|
|
| East Coast Sea Nettle |
Other Sites:
East Coast Sea Nettle
Nettlesome Nuisance |
|
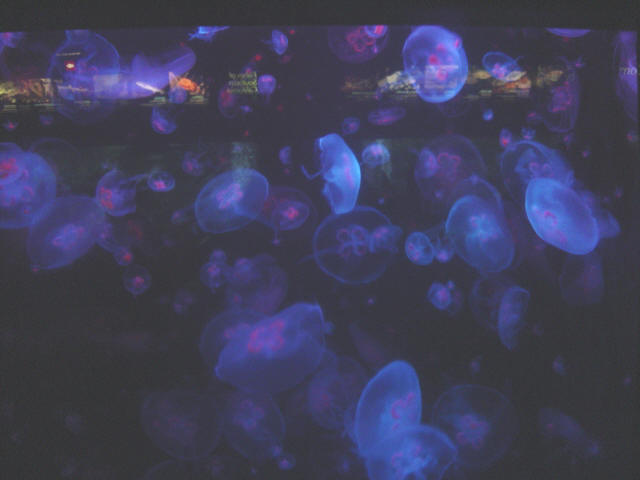

Picture by Mrs. Fox taken at Shedd Aquarium |
| Habitat: worldwide in temperateand tropical waters. Size: up to 15 inches
Food: mollusks, crustaceans, fisheggs and other jellyfish
Interesting Fact: Moonjellies went into space on the Columbian
in 1991.
|
|
| Moonjellies in motion |
|